Conveyor systems help “convey,” or move, packages, food, products or equipment from area within a facility to another, usually for simple transportation or to perform the various stages of automated or semi-automated manufacturing or finishing. Read More…
At Interroll Atlanta LLC, we are dedicated to advancing the efficiency and performance of material handling operations through our innovative conveyor solutions. As part of a global organization with a strong reputation for engineering excellence, we focus on delivering systems that meet the highest standards of reliability and flexibility.
At Pack Air Inc., we help manufacturers design and build innovative custom conveyors in the United States and Canada. Our specialty resides in creating custom conveyor solutions and product handling devices that help solve conveying problems. We don’t try to force pre-made conveyors in a box. Rather, we let the box define the solution so that your conveyors fit right the first time.
At Akona Process Solutions, we take pride in designing and manufacturing conveyor systems that bring efficiency, reliability, and innovation to material handling. Our team understands the importance of precision, durability, and streamlined operation, so we engineer our conveyors to meet the diverse needs of industries ranging from manufacturing and processing to packaging and distribution.
At Liberty Conveyor, we are dedicated to delivering dependable conveyor systems that enhance efficiency and streamline operations across a wide range of industries. With years of expertise in conveyor technology, we design and manufacture solutions that are tailored to meet the demands of manufacturing facilities, warehouses, distribution centers, and specialized production environments.

At Transcon Conveyor, we take pride in designing and manufacturing conveyor systems that deliver lasting performance and reliability for even the most demanding industrial applications. With decades of experience in the field, we have built a reputation for engineering heavy-duty, custom-built conveyors that meet the unique needs of our customers across diverse industries.

At FATA Automation, we specialize in creating advanced conveyor systems and material handling solutions that help manufacturers and distributors streamline their operations and achieve higher levels of efficiency. We design, engineer, and manufacture conveyors that are customized to meet the demands of complex production lines, high-volume distribution centers, and intricate assembly environments.

Vecoplan leads the charge with cutting-edge technologies that revolutionize waste and recycling. From versatile shredders and granulators to efficient conveying and sorting systems, Vecoplan offers a wide array of solutions for handling wood, paper, plastics, textiles, and more. Our tailored equipment sets new industry standards, meeting the demands of even the most challenging applications.
More Conveyor Companies
Key Points
-
- Conveyors are mechanical systems designed to move materials or products efficiently, commonly used across a wide range of industries for material handling and automation.
- Research and industry use-cases demonstrate they enhance productivity, operational safety, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, retail, mining, agriculture, food processing, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and construction.
- The evidence strongly supports their adaptability, with specific conveyor designs like belt, roller, chain, and screw conveyors tailored to meet diverse industry requirements.
Introduction to Conveyors
Conveyors are mechanical devices or integrated systems that continuously transport materials, products, or even people from one location to another. Utilizing mechanisms such as belts, chains, rollers, or pneumatic tubes, they are essential components in modern material handling solutions. By automating the movement of heavy, bulky, or numerous items, conveyors reduce manual labor, improve throughput, and optimize operational efficiency in both manufacturing facilities and distribution centers.
Applications Across Industries
Conveyors play a pivotal role in a broad array of sectors, each leveraging their specific benefits to address unique operational challenges and objectives. Here’s an overview of key conveyor system applications by industry:
- Manufacturing: Streamlines production lines by moving raw materials, components, and finished products through various assembly and processing stages. For example, car frames are transported along automotive assembly lines, while circuit boards are precisely moved through electronics manufacturing.
- Warehouses and Distribution: Enables high-speed sorting and routing of packages, integrates with automated picking systems, and maximizes order fulfillment efficiency in environments such as e-commerce fulfillment centers and distribution hubs.
- Retail: Supports checkout operations in supermarkets and facilitates baggage handling systems at airports, ensuring quick and reliable transactions for customers.
- Mining: Transports ore, coal, and other minerals over long distances, often in harsh or remote environments. Conveyor systems in mining reduce reliance on trucks, lower transportation costs, and enhance safety.
- Agriculture: Handles bulk grains and livestock products, streamlining post-harvest handling, storage, and processing with minimal manual intervention.
- Food Processing: Moves products through cleaning, sorting, cutting, cooking, and packaging stages, utilizing hygienic conveyor designs to meet strict food safety standards.
- Pharmaceuticals: Maintains controlled, sterile environments for the manufacturing and packaging of medications, ensuring regulatory compliance and precision.
- Automotive: Supports production operations in paint shops and assembly lines, as well as efficient auto parts distribution throughout manufacturing and supply chain facilities.
- Construction: Transports heavy construction materials such as concrete, bricks, and lumber to various levels of building sites, reducing manual lifting and improving site safety.
This diverse approach to conveyor system implementation allows for highly tailored solutions. Industries benefit from reduced workplace injuries, faster order processing, and scalable material handling workflows.
Detailed Description of Conveyor Applications Across Industries
Conveyor systems are recognized as foundational automation technologies in global industry, offering unparalleled versatility and reliability for material handling. This in-depth overview explores their broad applications and strategic importance across the manufacturing, logistics, retail, mining, agriculture, food processing, pharmaceutical, automotive, and construction sectors. Drawing on the latest insights and best practices as of 2025, the following sections will help buyers, engineers, and decision-makers understand how to select, implement, and optimize conveyor systems for their operational goals.
Definition and Overview
A conveyor system is a mechanical assembly designed to efficiently transport materials, products, or people along a defined pathway—typically via continuous belts, chains, rollers, or other mechanisms. As highlighted by Wikipedia: Conveyor System and Ultimation: Conveyor Types, conveyors are essential in material handling, manufacturing, and packaging, driving productivity and automation.
Industries and Specific Applications
The following table summarizes key industries and their typical conveyor system applications, providing a quick reference for buyers and facility managers:
| Industry | Key Applications | Examples |
| Manufacturing | Moves raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished products through production stages | Car frames on assembly lines in automotive plants, circuit boards in electronics |
| Warehouses & Distribution | Sorts and routes packages, integrates with picking systems for order fulfillment | Package sorting in distribution centers, automated picking in e-commerce warehouses |
| Retail | Assists in customer transactions and luggage handling | Checkout conveyors in supermarkets, luggage belts at airports |
| Mining | Transports ore, coal, and minerals over long distances | Moving ore from mines to processing plants, reducing truck dependency |
| Agriculture | Handles grains, poultry, and other products for processing and storage | Grain transport to silos, poultry processing lines |
| Food Processing | Moves products through stages like washing, cutting, cooking, and packaging | Conveyors for meat processing, ensuring hygiene with stainless steel designs |
| Pharmaceuticals | Ensures controlled environments for manufacturing and packaging medications | Transporting bottles through filling and sealing stages, maintaining sterility |
| Automotive | Supports paint shops, assembly lines, and parts distribution | Moving car bodies through paint drying, distributing auto parts in warehouses |
| Construction | Transports materials like concrete, bricks, and lumber to building sites | Conveying concrete to upper floors, reducing manual lifting for safety |
Detailed Industry Applications
- Manufacturing Industry
In manufacturing, conveyor systems are integral for moving materials and products through each stage of the production process. Whether it’s automotive assembly (car frames, engines, doors) or electronics manufacturing (printed circuit boards for soldering, inspection, and testing), conveyors create a seamless, continuous workflow that reduces bottlenecks and manual handling. Modern manufacturing plants rely on automated conveyors to enable just-in-time (JIT) production, minimize wait times, and ensure consistent product quality. For more, see Cablevey Conveyors: Types of Conveyors.
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers
Conveyors underpin efficient order fulfillment, shipping, and receiving operations. Advanced systems integrate with robotics, barcode scanners, and warehouse management software (WMS) to direct packages to the correct shipping lanes, automate picking, and maximize throughput. E-commerce giants and third-party logistics providers depend on conveyor automation to meet high order volumes and fast delivery expectations. Learn more at Conveyco: What is a Conveyor System?.
- Retail Industry
Retailers utilize conveyors for customer-facing and back-end operations. Supermarket checkout conveyors streamline transactions, while airports deploy conveyor belts for efficient baggage handling from check-in through security and onto aircraft. These systems improve speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
- Mining Industry
Mining operations depend on conveyors to safely and efficiently transport ore, coal, and minerals from extraction points to processing plants or storage areas. By minimizing truck usage, conveyors reduce operational costs and lower environmental impact. They also improve mine safety by reducing vehicle traffic in hazardous environments. See more at IQS Directory: Conveyor System.
- Agriculture Industry
Agricultural conveyors move harvested crops to silos, transport poultry through processing lines, and facilitate bulk material handling for fertilizers, feed, and grains. By automating these tasks, conveyors minimize post-harvest losses and enhance hygiene in food production. Reference: Gough Econ: Types of Manufacturing Conveyors.
- Food Processing Industry
Conveyor systems in food production are engineered with sanitary design principles, utilizing stainless steel frames and easy-to-clean surfaces. They move ingredients and finished goods through washing, slicing, cooking, cooling, and packaging stages while maintaining strict hygiene and traceability. See REB Storage Systems: Material Handling Conveyors.
- Pharmaceutical Industry
Precision and compliance are critical in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Conveyor systems enable controlled, contamination-free environments for the transport of bottles, tablets, and vials through filling, capping, labeling, and packaging. Advanced sensors and vision systems ensure accurate handling and regulatory adherence. Source: Exotec: Guide to Conveyor Systems.
- Automotive Industry
Automotive conveyors extend beyond assembly lines to include specialized systems for paint shops, drying tunnels, and parts distribution. These conveyors support high-volume production, enable lean manufacturing, and ensure efficient inventory movement from suppliers to the factory floor. For practical guidance, visit Conger Industries: What is a Conveyor?.
- Construction Industry
In construction, conveyors deliver heavy materials like concrete, bricks, and lumber to high-rise buildings and hard-to-reach locations, improving site safety and speeding up complex projects. These systems are often portable and adaptable to evolving site layouts, as highlighted by Cablevey Conveyors: Industrial Conveyor Systems.
Benefits and Adaptability
Conveyor systems deliver critical benefits, including increased productivity, reduced labor costs, enhanced workplace safety, and improved process consistency. By minimizing manual lifting and repetitive movements, conveyors lower the risk of musculoskeletal injuries and create a safer work environment. Their adaptability is demonstrated by a wide variety of available designs—belt, roller, chain, screw, pneumatic, and more—each suitable for specific materials and operational requirements.
Looking for the right conveyor for your industry? Explore our conveyor manufacturer listings or contact us for custom recommendations.
Conveyor System Applications
Modern conveyor systems are foundational to process automation, logistics optimization, and supply chain management. Below are some of the most prominent application areas:
- Production Line Automation: Ensures continuous material flow, reduces wait times between stations, and supports lean manufacturing principles.
- Order Fulfillment and Sorting: Accelerates picking and packing operations in warehouses, integrating with automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) and robotics.
- Airport Baggage Handling: Automates the movement of luggage between terminals, security checkpoints, and aircraft, reducing lost baggage and improving passenger experience.
- Bulk Material Handling: Facilitates the efficient movement of large quantities of loose materials (ores, grains, aggregates) over long distances in mining, agriculture, and construction.
- Sanitary Material Transfer: Maintains cleanliness and compliance in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical production.
Curious about which conveyor system best fits your facility? Ask: “Which conveyor types are best for my specific application?” or “How can conveyor automation improve my warehouse efficiency?”
History of Conveyor Systems
The evolution of conveyor systems reflects the broader history of industrial automation and material handling innovation:
- 1795: The first conveyor system, using leather belts and wooden frames, facilitated loading agricultural products onto ships.
- 1804: Steam-powered conveyor belts were adopted by the British Navy for shipboard biscuit production.
- 1892: Thomas Robins’ inventions revolutionized mining material handling with the first conveyor belts for ore and coal.
- 1901-1908: Innovations such as steel belt conveyors and the roller conveyor (with ball bearings) enabled smoother, more durable material transport.
- 1913-1919: Henry Ford’s assembly line conveyor transformed automotive manufacturing, leading to widespread adoption across industries.
- World War II: Synthetic materials like urethane and rubber were introduced, improving belt durability and performance.
- 1957: B.F. Goodrich’s “half-twist” conveyor belt improved wear distribution, though later superseded by advanced materials.
- 1970–present: Modular plastic conveyor belts and advanced automation have enabled highly customized, scalable systems. Modern conveyors can now span over 60 miles, as seen in the Western Sahara phosphate mine.
Want to learn more about conveyor system milestones? Search: “What are the key innovations in conveyor technology history?”
How Conveyor Systems Work
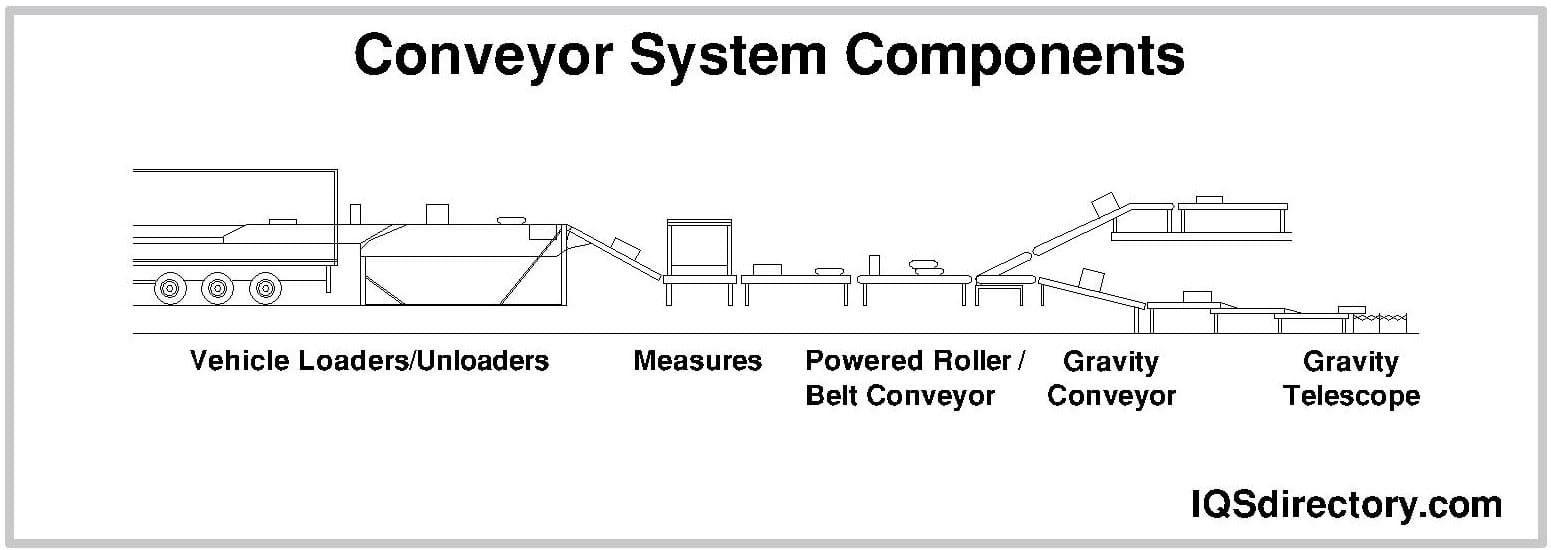
Conveyor systems operate by mechanically transporting items using interconnected belts, chains, rollers, or other mechanisms. Key components include:
- Conveyor Belt: Typically constructed of rubber, PVC, fabric, or metal, forming the continuous loop that carries items.
- Drive Unit: Electric motors or hydraulic systems provide the necessary power, driving pulleys or sprockets to move the belt or chain.
- Rollers and Idlers: Support and guide the belt, reducing friction and ensuring smooth movement.
- Tensioners and Take-up Units: Maintain proper belt alignment and tension.
- Control Systems: Include sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and speed adjusters for precise movement, sequencing, and safety control.
Optional attachments—such as trays, buckets, or cleats—enable the transport of bulk materials, delicate items, or products requiring specific orientation. Modern conveyor systems may also integrate with vision systems, barcode readers, and robotic arms for advanced automation.
Need help understanding conveyor mechanics? Try searching: “How does a conveyor belt system work?” or “What conveyor components are essential for reliable operation?”
Types of Conveyor Systems
A wide variety of conveyor types are available, each engineered for distinct material handling challenges and environments. Below is an expanded guide to common conveyor system types and their ideal use-cases:
- Belt Conveyors: The most widely used conveyor type, ideal for linear transport of bulk materials, boxes, and small products. Available in various materials for different environments, including food-grade and heat-resistant belts.
- Pallet Conveyors: Specially designed belt conveyors for heavy loads such as pallets and grid boxes, often used in manufacturing and warehousing.
- Timing Belt Conveyors: Feature toothed belts and pulleys for precise product positioning and accurate indexing, commonly used in electronics and assembly operations.
- Chain Conveyors: Employ chains to move large, heavy, or hot items, such as metal parts through washers or ovens. Popular in automotive and metalworking industries.
- Roller Conveyors: Use parallel rollers to move items, ideal for flat-bottomed goods, cartons, and equipment. Can be powered or gravity-fed.
- Spiral Conveyors: Move products vertically using spiral belts or slats, often found in food, beverage, and parcel handling for space-efficient elevation.
- Overhead Conveyors: Transport items above the work area, freeing floor space and integrating with painting, drying, or assembly lines. Used extensively in automotive and appliance manufacturing.
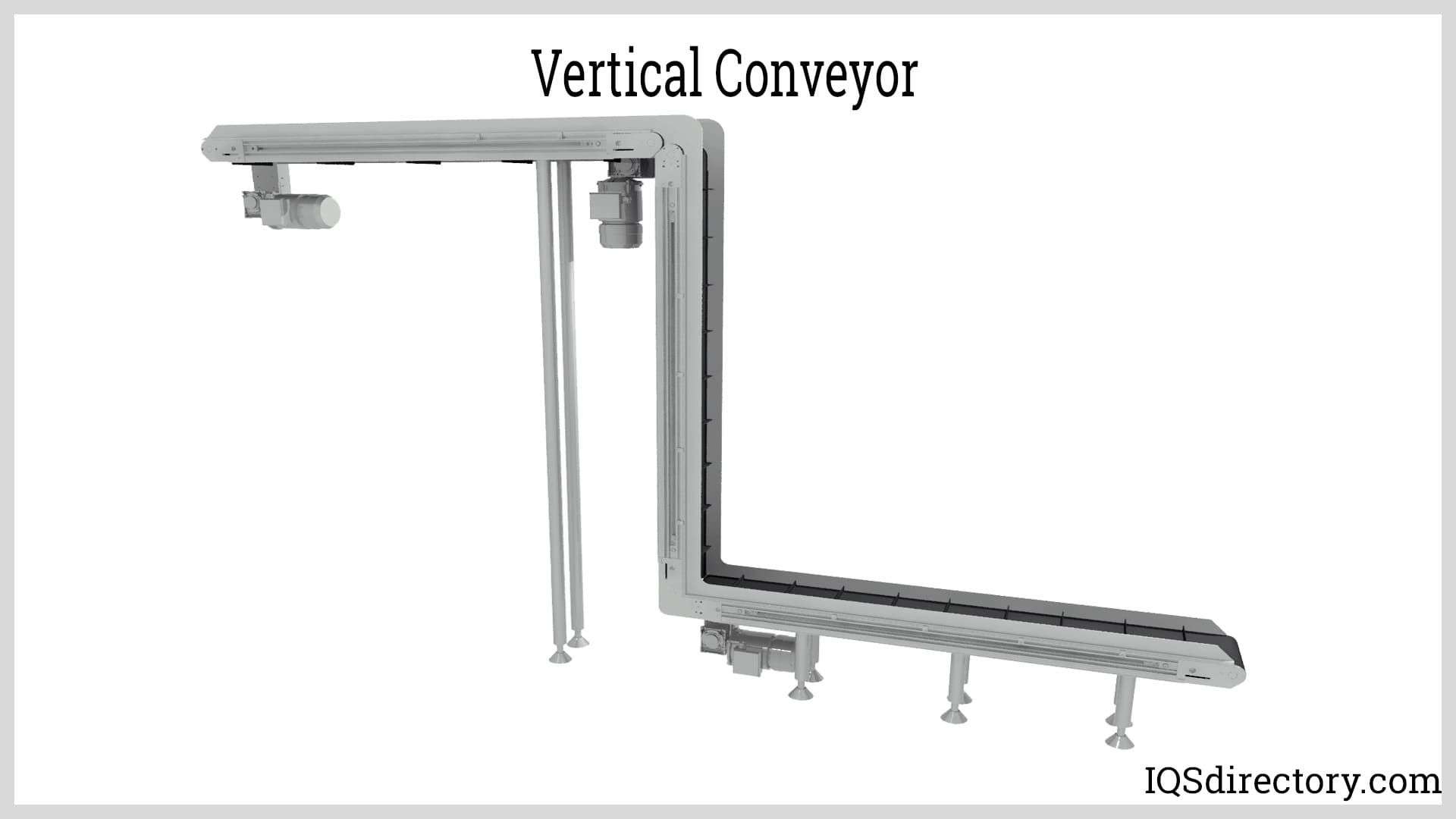
- Vertical Conveyors: Lift materials between facility levels, using platforms, grippers, or bucket elevators. Essential for multi-story warehouses.
- Food Conveyors: Built from sanitary stainless steel and equipped with features like weight scales, metal detectors, and robotic sortation. Designed for compliance with FDA and USDA requirements.
- Industrial Conveyors: Broad category encompassing systems for manufacturing, packaging, and assembly, adaptable to various materials and products.
- Gravity Conveyors: Rely on incline and gravity rather than motors for movement—ideal for lightweight packages or as flexible extensions to powered lines.
- Gravity Roller & Wheel Conveyors: Cost-effective solutions for horizontal or inclined movement, often used in shipping and receiving areas.
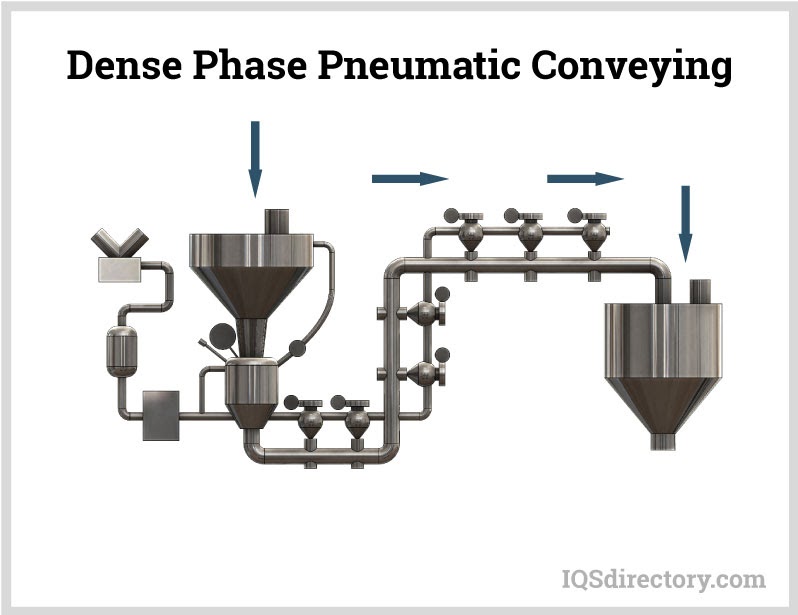
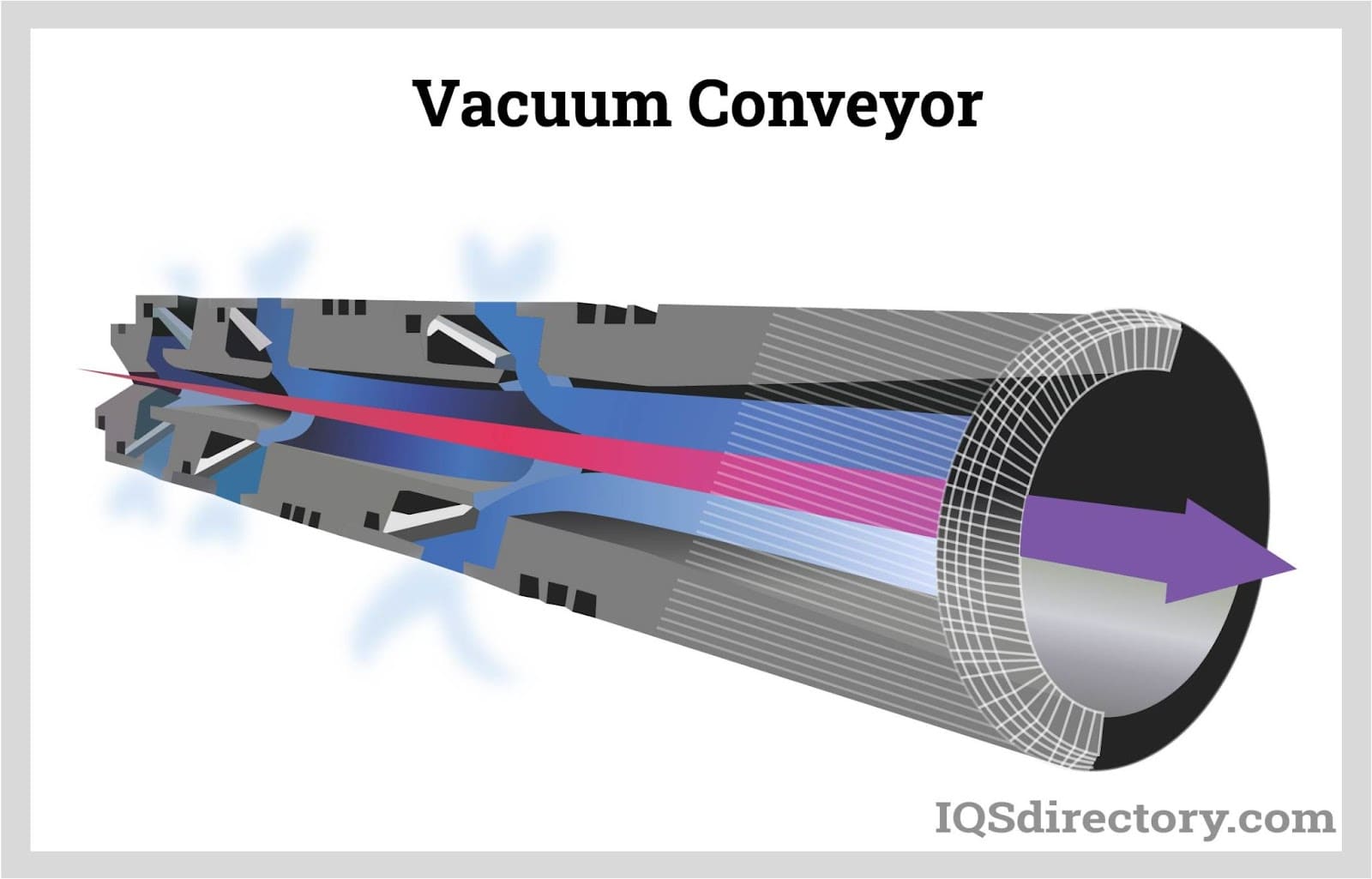
- Pneumatic Conveyors: Move powders or granulated materials through sealed pipelines using air flow—ideal for pharmaceuticals, food, and chemical processing.
- Screw Conveyors: Utilize rotating screws to move semi-dry or bulk granular materials horizontally or vertically—commonly found in agriculture, food processing, and mining.
- Modular Conveyor Systems: Offer unmatched flexibility, allowing reconfiguration and expansion as facility needs change. Built from lightweight, high-impact polycarbonate and compatible with a variety of belt and drive types.
Not sure which conveyor system is best for your materials? Search: “What conveyor system is right for my industry?” or “How do I choose between belt, chain, and roller conveyors?”
Benefits of Conveyor Systems
The adoption of conveyor systems provides substantial operational benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated transport reduces manual labor, accelerates workflows, and minimizes production and distribution bottlenecks.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of injuries by limiting manual material handling, repetitive motion, and heavy lifting. Integrated safety features (emergency stops, sensors, guards) further protect operators.
- Improved Accuracy: Consistent, precise movement ensures correct product orientation, reduces handling errors, and supports high-quality output.
- Maximized Space Utilization: Flexible layouts, including vertical and overhead conveyors, optimize available floor space and increase storage capacity.
- Superior Traceability: Integration with barcode/RFID scanning enables real-time inventory tracking, improves recall management, and supports regulatory compliance.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automated systems lower labor costs and energy consumption over time, providing cost-effective long-term solutions.
- Scalability and Customization: Modular designs and custom engineering allow systems to grow and adapt with changing operational needs.
Considering a conveyor system for your facility? Try searching: “What are the benefits of conveyor automation in my industry?” or “How can conveyors reduce operational costs and improve safety?”
Conveyor System Design and Customization
Modern conveyor design is highly customizable, supporting unique facility layouts, material types, and operational goals. Key design considerations include:
- Material Properties: Are items loose, fragile, heavy, hygienic, or abrasive?
- Required Throughput: How many units per hour or day?
- Facility Layout: Straight, curved, inclined, declined, spiral, or vertical routing?
- Integration: Will the conveyor system connect with robotics, packaging machines, or existing automation?
- Movement Mechanism: Belt, chain, roller, pneumatic, or screw?
- Compliance: Are there regulatory requirements (FDA, OSHA, ISO, Mil-Spec) to meet?
Manufacturers can provide portable, modular, clean-in-place (CIP), and heavy-duty options to match application needs. Whether you’re seeking a turnkey conveyor solution or a fully custom engineered system, it’s vital to communicate your specific goals and challenges.
Not sure how to begin your conveyor project? Ask: “How do I design a conveyor system for my facility’s needs?”
Conveyor System Safety and Compliance Standards
Conveyor systems must meet stringent safety and compliance standards, varying by application and jurisdiction:
- Food Processing: FDA, USDA, and HACCP compliance for sanitary conveyors.
- Industrial: ANSI, ASME, and OSHA standards for mechanical safety and guarding.
- Mining & Heavy Industry: MSHA regulations and CEMA standards for mining conveyors.
- Global Operations: ISO standards for quality management and system reliability.
Adhering to relevant regulations not only ensures worker safety but also reduces liability and supports product quality.
Want to verify compliance? Search: “What conveyor safety standards apply to my industry?”
How to Choose the Right Conveyor System Manufacturer
Key Points
- Effective conveyor system selection starts with defining your operational needs, researching suppliers, and evaluating them based on quality, experience, and after-sales support.
- Crucial decision factors include reputation, customization capabilities, technology, compliance, and long-term service and maintenance.
- Consider the total cost of ownership—including maintenance, energy efficiency, and scalability—when comparing manufacturers.
Define Your Needs
Begin by detailing the materials to be moved, required capacity, physical constraints, and budget. Clarify whether you need a standard solution or a custom system, what regulatory standards must be met, and if integration with existing automation is required. This early planning is critical for narrowing down suitable conveyor types and suppliers.
Research Manufacturers
Search online directories, consult industry associations (like CEMA), attend trade shows (e.g., ProMat, MODEX), and seek recommendations from peers with relevant experience. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and the specific conveyor technologies you need.
Evaluate and Choose
Compare suppliers on product quality, engineering expertise, customer service, customization ability, and value for money. Check for ISO certifications, customer references, and examples of similar successful installations. Visit their facilities or request demonstrations when possible.
Detailed Description of How to Choose the Right Conveyor System Manufacturer
Selecting a conveyor system manufacturer is a strategic investment. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure success:
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| Define Your Requirements | Determine the conveyor type, required throughput, and application-specific features. | Material properties, system layout, compliance, integration, budget. |
| Research Potential Manufacturers | Identify candidates via directories, associations, and trade networks. | Industry specialization, reputation, peer reviews, technology offerings. |
| Evaluate Manufacturers | Assess quality, experience, customization, and support. | Certifications, case studies, warranty, after-sales service. |
| Narrow Down the List | Shortlist based on critical requirements and past performance. | Relevant expertise, positive references, transparent pricing. |
| Request Detailed Quotes | Share detailed specs for accurate proposals. | Lead time, installation, training, support, scalability. |
| Visit or Demonstrate | Arrange site visits or demos to review real-world performance. | Quality assurance, operational fit, integration ease. |
| Make a Decision | Weigh total value, not just price. | Long-term ROI, maintenance, upgradeability. |
| Formalize the Agreement | Draft a comprehensive contract covering all terms. | Scope, timeline, warranty, legal compliance. |
Unexpected Considerations: Evaluate the manufacturer’s financial stability and parts availability. A stable partner ensures ongoing support, reliable warranty fulfillment, and timely access to replacement parts, minimizing downtime risk.
Sample Questions to Ask Manufacturers:
- Can you provide references or case studies from similar projects?
- What is your average lead time for custom conveyor systems?
- Do you offer installation, commissioning, and training services?
- How do you handle warranty claims and ongoing support?
- What are your policies on spare parts and maintenance contracts?
Real-World Examples:
- Kentucky Distillery: Needed high-capacity, food-grade grain conveyors. Chose a manufacturer with ISO 9001 certification and strong hygiene compliance, resulting in efficient, reliable grain handling.
- Indiana CNC Shop: Sought a scalable parts distribution system. Chose a local manufacturer with strong integration support, leading to reduced lead times and smooth automation rollout.
- Mississippi Food Processor: Required hygienic conveyors for meat processing. Prioritized FDA compliance, after-sales service, and maintenance contracts for seamless, safe operations.
Benefits and Best Practices: The right manufacturer delivers enhanced operational efficiency, lower total costs, and long-term system reliability. Lean on industry resources, prioritize transparent communication, and focus on total cost of ownership—not just upfront expenses—when making your decision.
Conclusion: Choosing the right conveyor system and manufacturer is essential for maximizing productivity, ensuring safety, and achieving sustainable growth in today’s competitive industrial landscape. By following a systematic selection process and partnering with a reputable conveyor supplier, you can confidently implement material handling automation that will benefit your operations for years to come.
Ready to get started? Explore our curated conveyor manufacturer listings, or contact us for personalized assistance and expert advice on your next conveyor system project.
What is a conveyor system and how does it work?
A conveyor system is a mechanical setup designed to move materials, products, or people from one point to another using belts, rollers, chains, or pneumatic tubes. It operates by transporting items along a predetermined path, utilizing components such as belts, drive units, rollers, tensioners, and control systems for efficient and automated material handling.
Which industries commonly use conveyor systems?
Conveyor systems are widely used in manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, retail, mining, agriculture, food processing, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and construction industries. Each industry leverages conveyors for specific tasks such as assembly, material transport, product handling, and process automation.
What are the different types of conveyor systems?
Conveyor systems come in a variety of types, including belt conveyors, pallet conveyors, timing belt conveyors, chain conveyors, roller conveyors, spiral conveyors, overhead and vertical conveyors, food conveyors, industrial conveyors, gravity conveyors, gravity roller and wheel conveyors, pneumatic conveyors, screw conveyors, and modular conveyor systems. Each type is engineered for specific material handling challenges and environments.
What are the main benefits of using a conveyor system?
Conveyor systems increase efficiency, reduce manual labor, enhance safety, improve product handling accuracy, maximize space utilization, enable better traceability, reduce operational costs, and support scalability through modular and customizable designs. These benefits lead to higher productivity and safer work environments.
How do I choose the right conveyor system for my application?
Choosing the right conveyor system involves considering material properties (weight, fragility, hygiene), capacity, facility layout, throughput requirements, integration needs, and compliance with safety or industry regulations. It’s recommended to define your operational goals clearly and consult with suppliers experienced in your industry for customized solutions.
What safety and compliance standards apply to conveyor systems?
Conveyor systems must meet industry-specific and national safety standards such as FDA, USDA, and HACCP for food processing; ANSI, ASME, and OSHA for industrial applications; MSHA and CEMA for mining; and ISO standards for quality and reliability in global operations.
How should I select a conveyor system manufacturer?
Select a manufacturer by defining your conveyor requirements, researching potential suppliers, evaluating them on quality, customization, experience, compliance, service, and total cost of ownership. Ask about their certifications, references, warranty, after-sales support, and review case studies to ensure they can meet your needs reliably.
What are some prominent application areas for conveyor systems?
Key application areas include production line automation, order fulfillment and sorting, airport baggage handling, bulk material handling in mining and agriculture, and sanitary material transfer in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. Conveyors can be integrated with robotics and automated storage systems for advanced operations.
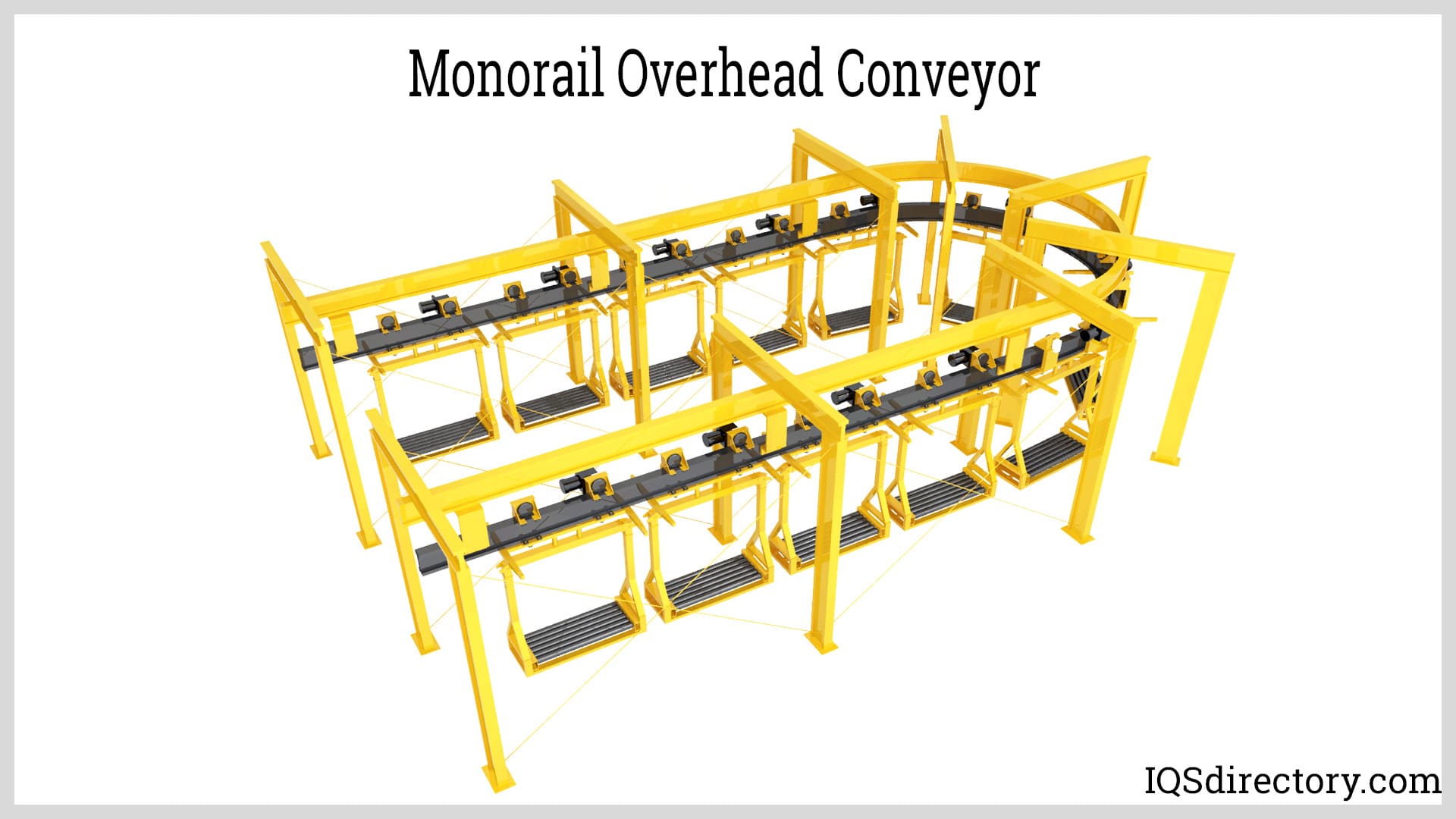
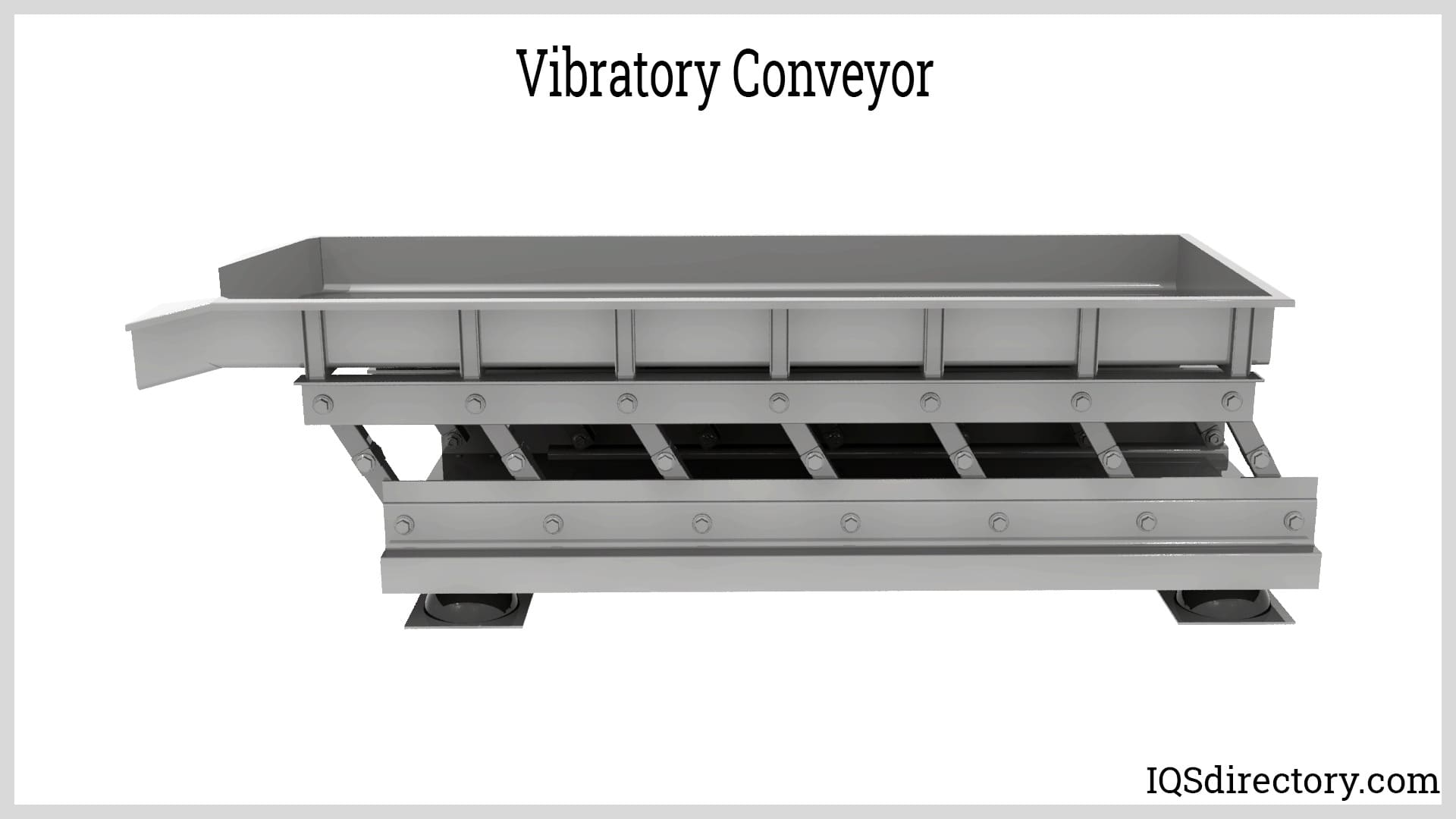







 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting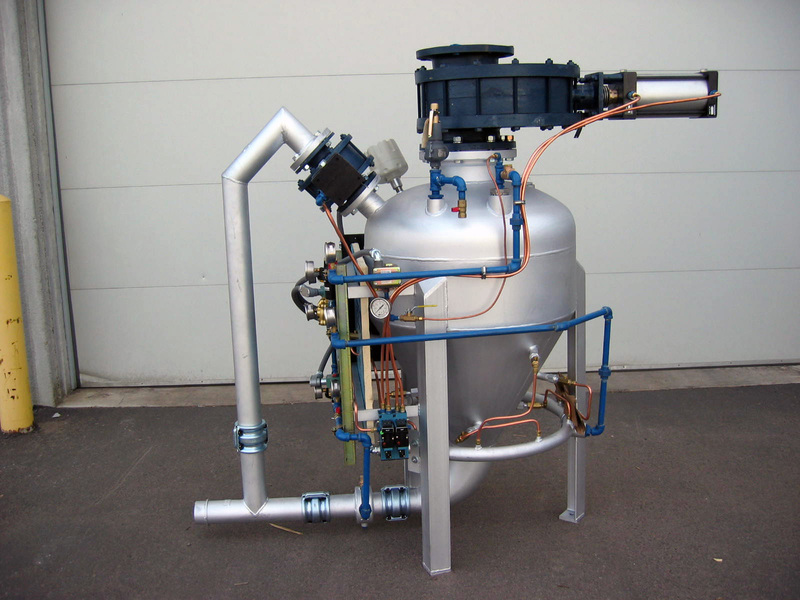 Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators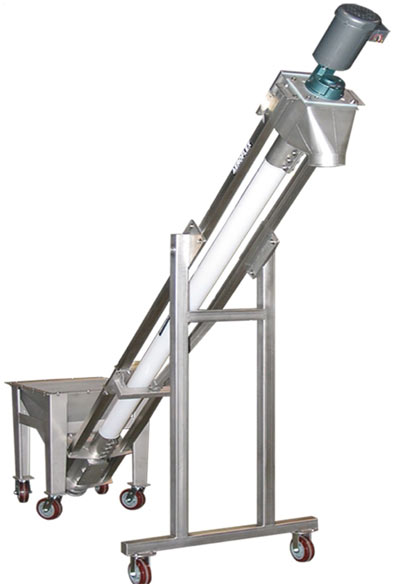 Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches